
Thermochemistry:
EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC REACTIONS
Exothermic Reactions:
DEFINITION: Exothermic Reaction
An exothermic reaction is one which gives out energy to the surroundings, usually in the form of heat and usually shown by a rise in temperature.
Examples of Exothermic Reactions:
- Combustion
- Neutralisation reactions
- Hydration of anhydrous copper sulphate
Endothermic Reactions:
DEFINITION: Endothermic Reaction
An endothermic reaction is one which takes in energy from the surroundings, usually in the form of heat and usually shown by a fall in temperature.
Examples of Endothermic Reactions:
- Photosynthesis
- Dissolving certain salts in water (e.g. potassium chloride, ammonium nitrate)
- Thermal decomposition (e.g. converting calcium carbonate into calcium oxide (quicklime))
ENTHALPY CHANGE
ΔH (read as 'delta H') is the symbol for the enthalpy change of a reaction. Enthalpy change refers to the change in energy in a reaction. ΔH is negative for an exothermic reaction (i.e. the products have less energy than the reactants) and positive for an endothermic reaction (i.e. the product have more energy than the reactants).
- ΔH is negative for exothermic reactions
- The difference in energy is given out as heat.
- Therefore, the temperature rises.
- ΔH is positive for endothermic reactions
- The extra energy needed to form the products is taken in from the surroundings.
- Therefore, the temperature falls.
Energy Level Diagrams:
Enthalpy change can be illustrated using an energy level diagram:
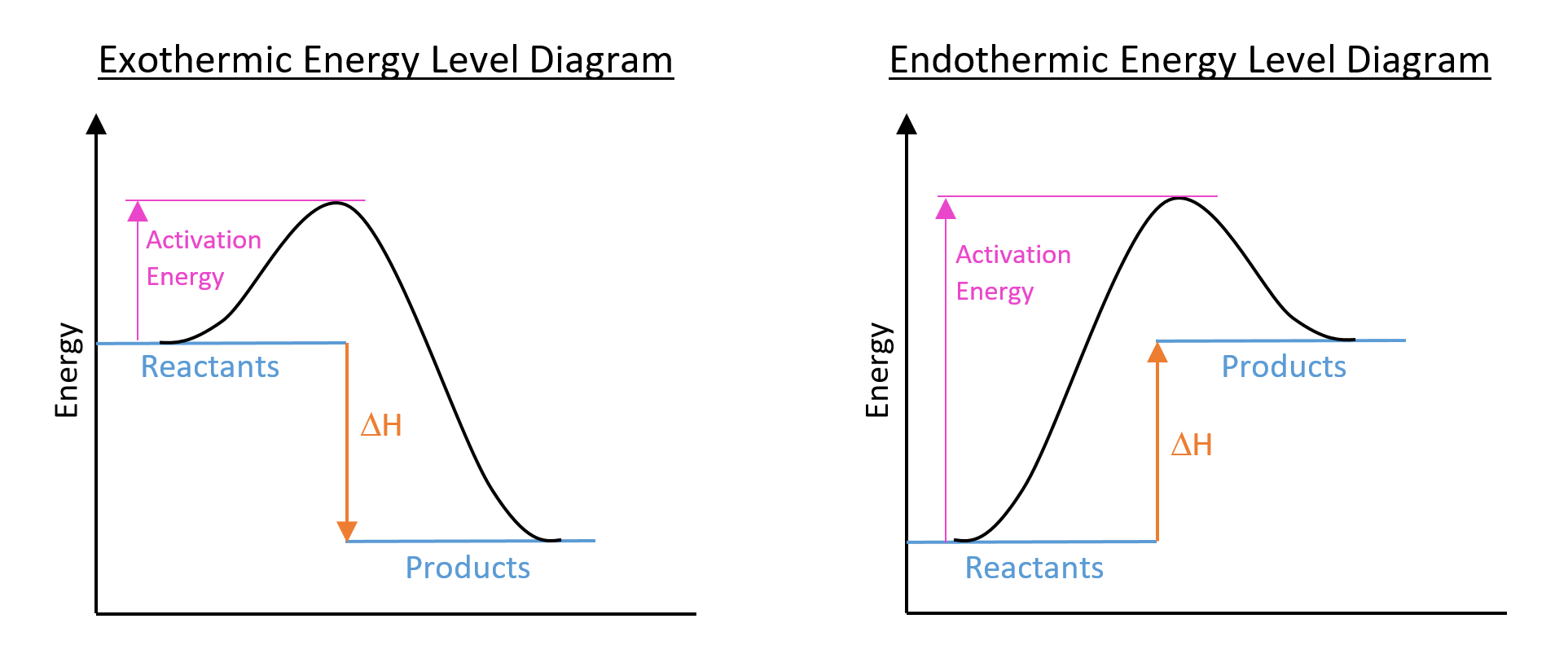
Sometimes, a simplified version of the above diagrams are drawn, without the reaction pathway curve and activation energy drawn on.
DEFINITION: Activation Energy
Activation energy is the minimum energy required for reactants to undergo a chemical reaction. It can be lowered by using a catalyst.
CALORIMETRY CALCULATIONS
Formula for Energy Change:
`q = mcDeltaT`
Where:
`q` = energy change
`m` = mass of water
`c` = specific heat capacity
`DeltaT` = temperature change
Specific Heat Capacity (c) is the quantity of energy, in Joules (J), needed to change the temperature of one gram (g) of a substance by one degree Celsius (oC).
e.g. The specific heat capacity of water is 4.18 J/g/oC
Formula for Enthalpy Change:
`DeltaH = -q/n`
Where:
`DeltaH` = enthalpy change
`q` = energy change
`n` = number of moles
BOND ENERGY
We can work out the energy needed to break different chemical bonds. This is called the bond energy. These bond energies can be used to calculate ΔH for a reaction.
DEFINITION: Bond Energy
Bond energy is the amount of energy required to break one mole of a stated bond, measured in kJ/mol. It can be used to calculate ΔH for a reaction.
Bond energies are average values for the bonds in different molecules. Therefore, these calculations only give us a rough value for ΔH.
Making bonds is EXOTHERMIC
Breaking bonds is ENDOTHERMIC
Back to Chemistry Home